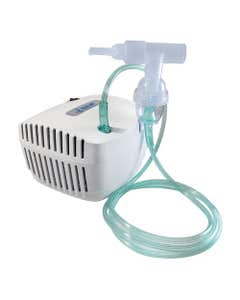
Nebulizers are used for managing a range of respiratory illnesses. A nebulizer converts prescribed respiratory medications into a fine mist that is more easily inhaled. Patients with asthma, COPD, and related lung diseases rely on a nebulizer for treating sudden attacks of shortness of breath.
Nebulizers are available in different types depending on the needs of the patient. Nebulizers are especially beneficial to children with respiratory illnesses because of their ease of use.


What is Nebulizer Treatment?
Nebulizer treatment is preferred for many types of patients with a respiratory illness because of the direct and immediate delivery of the medication. The misting of medication allows patients to inhale the medicine faster and more easily. Nebulizers are the best choice for dealing with sudden symptom events such as shortness of breath or wheezing, where immediate relief is needed.
Benefits of Nebulizer Treatments
Nebulizers are the best solution for managing symptom episodes. Patients with asthma or COPD may experience alarming attacks that require immediate relief. A nebulizer can provide relief sometimes faster and better than an inhaler. Because of their ease of use, they can be used by young children with respiratory illness.
Risks of Nebulizer Treatments
Because nebulizers mist the medication there is an increased risk of inhaling other airborne contaminants that can be harmful. This risk, however, is low if directions for use are followed by the patient. There are some side effects from the use of nebulizers reported among some patients including rapid heartbeat, anxiety, dizziness and vomiting.
These symptoms may be due to the more immediate ingestion of the medication or due in some instances to a reaction to the medication itself. Patients should speak to their doctor if they have any side effects.
Who Needs a Nebulizer?
A doctor may recommend a nebulizer to patients with asthma, COPD or other respiratory illnesses such as cystic fibrosis or chronic bronchitis. If patients currently struggle with the use of inhalers, nebulizer may be a better alternative for treatment. Children may find nebulizers easier to use than inhalers and in some severe cases of asthma or COPD a nebulizer may be more helpful in treating symptoms.
What Do You Put in a Nebulizer?
Medicines used in nebulizers include:
- Bronchodilators: designed to relax the airway and make breathing easier.
- Corticosteroids: reduce inflammation in the airway which can obstruct normal breathing.
- Hypertonic saline: loosen mucus secretions which can impair breathing.
- Mucolytic agents: break down thick mucus which obstructs breathing.
In addition to this common list, other medications such as antibiotics can also be used with a nebulizer based on a doctor’s recommendation.
How Do You Use a Nebulizer?
There are different types of nebulizers, but in general, they operate similarly. Follow these simple steps:
- Add the prescribed medicine to the medicine cup.
- Assemble the tubing and mouthpiece/mask (if applicable).
- Attach the tubing to the nebulizer.
- Turn the nebulizer on.
- Insert the mouthpiece or apply the mask and take slow, deep breaths.
Be sure to clean the medicine cup after each use.
Do You Need a Prescription to Use a Nebulizer?
Nebulizers are available over the counter. However, the medications used in a nebulizer will require a prescription from your doctor. Speak to your doctor about your respiratory concerns before purchasing a nebulizer. Some ailments can be managed efficiently with an inhaler. If your doctor prescribes nebulizer medication, you can ask about the type of nebulizer that best fits your needs.
Why Can I Buy a Nebulizer?
You can find nebulizers at most medical supply retailers. You can also shop online to explore different types of nebulizers available. Online shopping is fast and easy, and gives you the most options for your nebulizer purchase. You can find different types of nebulizers at The Oxygen Concentrator Supplies Shop. Our expert staff can help you select a nebulizer that will best help your respiratory condition.